VoX is an acronym for Voice eXchange.
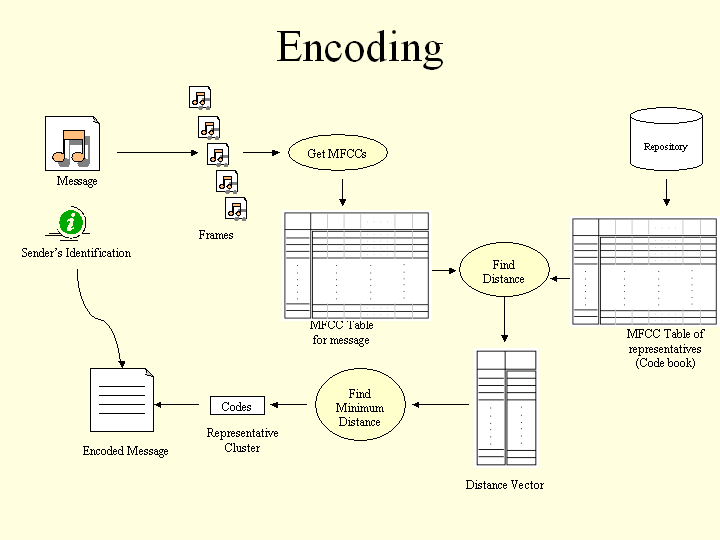
VoX is a nifty command-line based tool that is used to encode speech files using a repository.

The repository is created using a training file that contains a phonetically balanced speech of the trainer. This speech must be presented to the tool in Microsoft Wave format, recorded at 8KHz., with 16 bits per sample. The repository contains pieces of the trainer's voice and certain parameters associated with those pieces. The repository thus, represents the speech profile of a person. This profile is identified by the email-id of the creator.

At present only those messages that are in Microsoft Wave format can be encoded. The message must be recorded at 8KHz., with 16 bits per sample. The message is then encoded into a coded binary file.
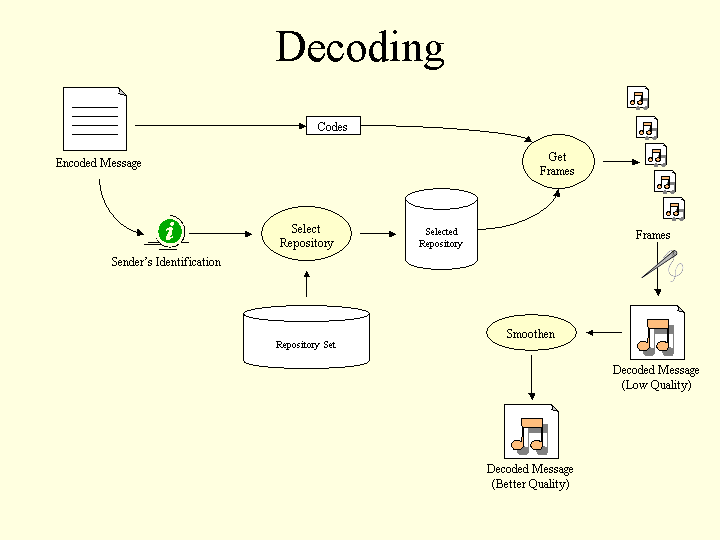
For the decoder to decode the message, the sender's repository must be available at the receiver's end.The output of the decoder is the reconstructed message in Microsoft Wave format sampled at 8KHz., with 16 bits per sample.
Advantages:
- Modest Bandwidth Requirements as only codes are transmitted instead of actual speech
- Spoken Communication is Expressive
Limitations:
- Single Speaker's Voice
- Large Number of Small Files
- Empirically Decided Cluster Cardinality
- Frame Length is Fixed
Application:
- News Broadcast and Archival
- As an E-mail Add-on (as in the block diagrams above)
Future Scope:
- Towards Unification and Generalization (The reverse of Personalization)
- Streamability (Real-time Communication)
VoX is registered under GNU Public Licence (GPL). More info can be obtained on the
project page.






